Namkha Khyung Dzong

Namkha Khyung Dzong (Tib. ནམ་མཁའ་ཁྱུང་རྫོང་, Wyl. nam mkha' khyung rdzong), the “Space Garuda Fortress”, in Tibet, is the name of a Dharma encampment founded on the slopes of Mount Kailash, in Western Tibet, by Degyal Rinpoche, one of the main students of Dudjom Lingpa.
Origins
In 1904, after Dudjom Lingpa left this world, a group of disciples, including Degyal Rinpoche and Ling Lama Chöjor Gyatso, went to Pemakö to discover the new incarnation of their teacher, Dudjom Rinpoche, who was only three years old at that time.
After one month in Pemakö, Degyal Rinpoche left for a pilgrimage to Central Tibet and then after to Western Tibet. Settling on the slopes of Mount Kailash, he spent most of his life in meditation.
When Degyal Rinpoche arrived at the base of the Mount Kalaish with some disciples, he did a retreat for three years at a place called the “Elephant Cave”, a meditation place used in the past by Guru Rinpoche.
After that, Degyal Rinpoche stayed two years in another cave located in the west side of Lake Manasarovar. Then, it is said that the “local gods appeared to welcome him on the “Crystal cave”, located in the south-west of Mount Kalaish. He accepted their invitation and decided to settle there permanently”.
Developments
The Arrival of Degyal Rinpoche in the Area
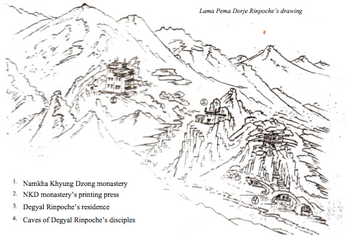
At first, Degyal Rinpoche stayed in retreat three different places, all of them located in the area of what was to become Namkha Kyung Dzong.
- Zimphuk Ogma, The Lower Dwelling Cave, which is about 30-40 feet at the middle of the rock.
- Zimphuk Barma, The Middle Dwelling Cave, which is for half part inside the rock, and for the other half simply built up with a wall. It is very small cave.
- Zimphuk Gongma, The Upper Dwelling Cave, which is a simple retreat place, a Tsamkang, on the upper side of the mountain.
The Expansion of Namkha Khyung Dzong
Degyal Rinpoche’s disciples followed him. At the beginning, it was a small hermitage but this spiritual center became more and more important as Degyal Rinpoche’s fame spread far and wide. Many practitioners from all parts of Tibet and Ladakh, about 3,000 at the time, gathered there in order to receive teachings each summer, and to practise in strict retreat in caves during winter. Degyal Rinpoche’s cave became a small hermitage called Namkha Khyung Dzong. As many of the students wished to stay close to their teacher, the place was organized in the following way: the monks lived in the caves of Drakpo Barwar Yendrö; the nuns stayed in individual tents in Jomolung valley; the ngakpas—lay men and women practitioners—stayed in another place.
The rules enacted by Degyal Rinpoche were very strict in order to protect the discipline and harmony of the sangha. Thus, the disciples were not allowed to visit someone who stayed in another place without a special authorization and without being accompanied by a witness. With regard to the daily schedule, there was no time for gossip and distraction. Between the prayers and rituals performed together, the practitioners stayed in seclusion to devote the rest of their time to meditation. Such a spiritual environment was propitious to attain the accomplishments and it is said that many disciples reached high levels of realization.
Being Transformed Into a Monastery
After the death of Degyal Rinpoche, at the instigation of his senior-most disciple Golok Serta Rinpoche, the hermitage enlarged to become a monastery. A stupa was built to keep the embalmed body of Degyal Rinpoche and in 1943 an assembly hall for the religious ceremonies was completed. In 1955, a big prayer wheel was erected.
At its beginning, as Degyal Rinpoche was a monk, Namkha Khyung Dzong was mainly a monastic community. But with Golok Serta Rinpoche, the situation changed because a large number of his disciples were ngakpas like him, carrying a family life along with meditation practices.
The Dudjom Tersar lineage became strongly established in this area, and took the name Dudjom Töluk, the Tibetan appellation for the Upper[1] tradition of Dudjom Tersar.
The Unrest Times
The Chinese invasion put an end to this spiritual place. As the situation was becoming more and more dangerous, in 1959, all the community members decided to escape Tibet in order to save their lives and preserve the lineage. Soon, during the political turmoil, the monastery was completely destroyed by the Chinese.
Carrying on their backs the embalmed body of Degyal Rinpoche, lamas, monks, nuns and ngakpas crossed the India border. They stayed about two years in a refugee camp in Sandew, Uttar Pradesh, India, and went then to another camp in Orissa where they built a small temple along with a new stupa for the holy relics.
After its escape from Tibet, the Namkha Khyung Dzong community was scattered between Nepal and India. Yet, in Humla, a territory of the far North-West of Nepal, close to Mount Kailash, many disciples of Golok Serta Rinpoche gathered and built a small monastery called Namkha Khyung Dzong (Nepal). Thus, it is mainly in this area that the tradition of Namkha Khyung Dzong, the Dudjom Töluk [2] was maintained.
Recent Years
Despite the opportunities he had to settle in the West, the Second Degyal Rinpoche chose to stay with his wife and children in this remote area of Humla in order to devote his live to the preservation of the lineage and pass it entirely before his own death to his son Shiva Rinpoche, the reincarnation of Golok Serta Rinpoche.
It seems that no rebuilding of the monastery in Tibet has begun up to now.
Main Characters
- Degyal Rinpoche
- Golok Serta Rinpoche
- Lama Pema Dorje Rinpoche
- Second Degyal Rinpoche
- Tokden Paksam Gyatso
- Tsokhang Choktrul Tsewang Dorje
Notes
- ↑ Upper refers to ‘Western Tibet’, and more precisely to the area of Mount Kailash.
- ↑ According to Shiva Rinpoche [post on Facebook], 'Dudjom Töluk is the Tibetan appellation for the Upper tradition of Dudjom Tersar. Upper means Western Tibet and more precisely the area of Mount Kailash. Why that? Because it is here that Degyal Rinpoche – one of the heart sons of Dudjom Lingpa, born in Golok (Eastern Tibet) and an emanation of Bairotsana – had settled to spend his life in meditation. His cave became a small hermitage called Namkha Khyung Dzong and this hermitage gathered many disciples from various places of Tibet and Himalaya in order to receive teachings each summer and practice in retreat during winter. The most famous disciple of Degyal Rinpoche was Golok Serta Rinpoche who came also from Golok. It is striking to know that he was considered as an emanation of Yudra Nyingpo who was in the VIIIst century the main disciple of Bairotsana…, But about about the name of Namkha Khyung Dzong?, Outwardly, it refers to Degyal Rinpoche’s place and to his special lineage but inwardly, we can find signs of the true meaning in Dzogchen tantras and Longchenpas’ works:, In the seng ge rtsal rdzogs chen po’ rgyud, one of the seventeen tantras of the pith instructions section (man ngag sde), we can find the following verses:, chos nyid ming dang bral ba'i nam mkha' la, mtshan ma'i yul med rang snang gser gyi bya khyung lding, bcos ma ma yin rang gi bde ba 'byung, In the sky [namkha] that is the true nature of phenomena, free of labels, Soars the garuda [khyung] of awareness’s own manifestations, with none of what characterizes sense objects., It is uncontrived self knowing awareness that is experience as blissful., Here Namkha refers to the empty essence of the Base primordially pure, Khyung refers to the luminous nature which is spontaneously present and Dzong refers to the unceasing and all-pervading compassion which manifests as self knowing awareness (rang rig). The inseparability of those three aspects of the Base is Namkha Khyung Dzong., But Dzong is more especially explained in the self-commentary of the Treasury of Dharmadhatu [chos dbyings mdzod] by Longchenpa, Awareness is timelessly fashioned as the “fortress” [dzong] of the vajra heart essence.